区块链、DAO、DApp、DeFi、NFT、Crypto、GameFi...
什么是web3.0
2006年提出。当下,我们正在经历 web3.0 时代。而现在也正是在一个进化的阶段,但至于这只靴子具体能够落在哪,现在也没人知道。
当提到web3.0,总会提到加密货币,这是因为web3.0协议非常依赖加密。
Web3.0代币是创建去中心化网络的重要数字资产。
web3.0指代的并不只是你以为的加密货币
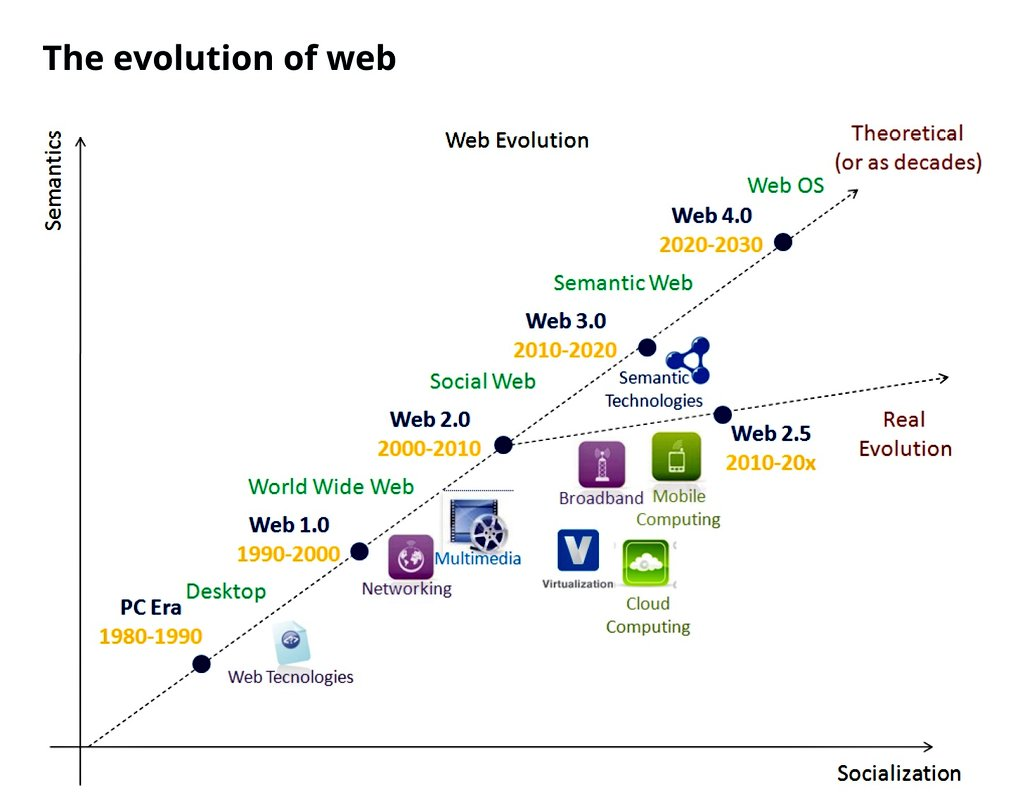
web发展史
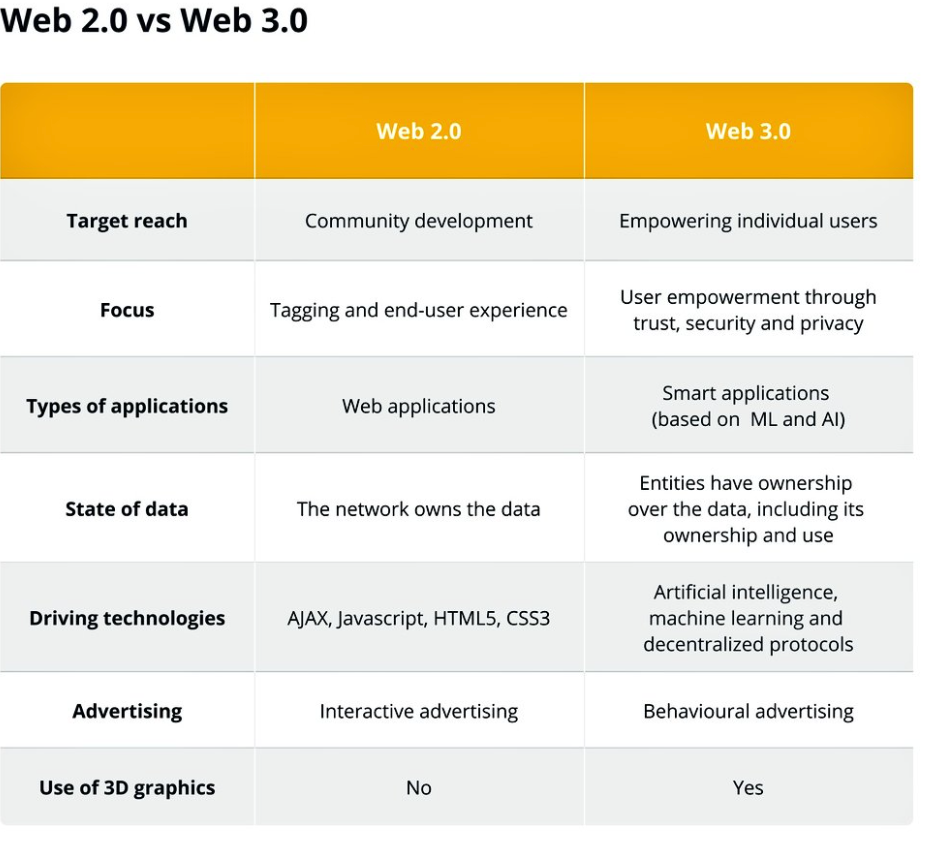
web3.0特点
web3.0核心特点
- 语义化的网络:互联网上的数据生产、搜索、分享等仅仅依赖语义本身
- 人工智能:将语义化的能力做到能够和人类互通,更智能化的提供信息
- 3D:博物馆指南、电脑游戏、电子商务、地理空间环境
- 互联:互联程度提升
- 无处不在:不仅仅依赖电脑和手机,IoT设备兴起
- 区块链技术:依赖加密技术,摆脱隐私泄露
- 去中心化:安全不被追踪
- 边缘计算

基于web3.0是一个人为控制 -> 无感情的机器管控。强调个人价值的回归。
在实际生产活动中,就可以发生一下场景,而这个也确实在发生的一个场景。
场景:在 Web 3.0 中,您可以在驾驶时向您的汽车助手提问:“我想看一部浪漫电影,吃日本料理。” 嵌入在汽车助手中的搜索引擎为您提供考虑您所在位置的个性化响应,通过自动查阅社交媒体上的评论(无利益相关),推荐与您的要求相匹配的最近电影院和一家不错的日本餐厅。 然后它甚至可以在显示屏上显示餐厅的 3D 菜单。

而在狭义层面理解,当前可以吧web3.0理解为去中心化的互联网生态。
web3.0 为啥会引人关注(个人观点)
- 传统的互联网野蛮生长,已经不存在,资本需要有资产标的。(包括元宇宙)
- 有个华丽的外衣,可以解决目前诟病的隐私、安全等互联核心存在的问题
- 隐私更强,也意味着一些见不得光的东西可以依附,比如洗钱等
- 一些不怀好意的恶意炒作(包括某些资本、马斯克)
All in crypto——资本
https://blockstream.com/ —— BTC生态
https://consensys.net/ —— ETH生态
当前主流的区块链
- 以太坊
- Hyperledger
- solana
- Polkdot
- Flow
- 蚂蚁链
我们在进行交易的时候,如何进行币种转化
- 选择一条链。通用协议,例如ERC2.0,以太坊ERC20,能够保证不同的代币之间可以直接进行互换。(注意有这个能力,不代表真实环境可以完成,因为还需要买方和卖方)
contract ERC20 {
// Maps user addresses to balances, similar to a dictionary in Cadence
mapping (address => uint256) private _balances;
function _transfer(address sender, address recipient, uint256 amount) {
// ensure the sender has a valid balance
require(_balances[sender] >= amount);
// subtract the amount from the senders ledger balance
_balances[sender] = _balances[sender] - amount;
// add the amount to the recipient’s ledger balance
_balances[recipient] = _balances[recipient] + amount
}
}- 部署自己智能合约(nft合约)
// This is a complete version of the ExampleNFT contract
// that includes withdraw and deposit functionality, as well as a
// collection resource that can be used to bundle NFTs together.
//
// It also includes a definition for the Minter resource,
// which can be used by admins to mint new NFTs.
//
// Learn more about non-fungible tokens in this tutorial: https://docs.onflow.org/docs/non-fungible-tokens
pub contract ExampleNFT {
// Declare Path constants so paths do not have to be hardcoded
// in transactions and scripts
pub let CollectionStoragePath: StoragePath
pub let CollectionPublicPath: PublicPath
pub let MinterStoragePath: StoragePath
// Declare the NFT resource type
pub resource NFT {
// The unique ID that differentiates each NFT
pub let id: UInt64
// Initialize both fields in the init function
init(initID: UInt64) {
self.id = initID
}
}
// We define this interface purely as a way to allow users
// to create public, restricted references to their NFT Collection.
// They would use this to only publicly expose the deposit, getIDs,
// and idExists fields in their Collection
pub resource interface NFTReceiver {
pub fun deposit(token: @NFT)
pub fun getIDs(): [UInt64]
pub fun idExists(id: UInt64): Bool
}
// The definition of the Collection resource that
// holds the NFTs that a user owns
pub resource Collection: NFTReceiver {
// dictionary of NFT conforming tokens
// NFT is a resource type with an `UInt64` ID field
pub var ownedNFTs: @{UInt64: NFT}
// Initialize the NFTs field to an empty collection
init () {
self.ownedNFTs <- {}
}
// withdraw
//
// Function that removes an NFT from the collection
// and moves it to the calling context
pub fun withdraw(withdrawID: UInt64): @NFT {
// If the NFT isn't found, the transaction panics and reverts
let token <- self.ownedNFTs.remove(key: withdrawID)!
return <-token
}
// deposit
//
// Function that takes a NFT as an argument and
// adds it to the collections dictionary
pub fun deposit(token: @NFT) {
// add the new token to the dictionary with a force assignment
// if there is already a value at that key, it will fail and revert
self.ownedNFTs[token.id] <-! token
}
// idExists checks to see if a NFT
// with the given ID exists in the collection
pub fun idExists(id: UInt64): Bool {
return self.ownedNFTs[id] != nil
}
// getIDs returns an array of the IDs that are in the collection
pub fun getIDs(): [UInt64] {
return self.ownedNFTs.keys
}
destroy() {
destroy self.ownedNFTs
}
}
// creates a new empty Collection resource and returns it
pub fun createEmptyCollection(): @Collection {
return <- create Collection()
}
// NFTMinter
//
// Resource that would be owned by an admin or by a smart contract
// that allows them to mint new NFTs when needed
pub resource NFTMinter {
// the ID that is used to mint NFTs
// it is only incremented so that NFT ids remain
// unique. It also keeps track of the total number of NFTs
// in existence
pub var idCount: UInt64
init() {
self.idCount = 1
}
// mintNFT
//
// Function that mints a new NFT with a new ID
// and returns it to the caller
pub fun mintNFT(): @NFT {
// create a new NFT
var newNFT <- create NFT(initID: self.idCount)
// change the id so that each ID is unique
self.idCount = self.idCount + 1 as UInt64
return <-newNFT
}
}
init() {
self.CollectionStoragePath = /storage/nftTutorialCollection
self.CollectionPublicPath = /public/nftTutorialCollection
self.MinterStoragePath = /storage/nftTutorialMinter
// store an empty NFT Collection in account storage
self.account.save(<-self.createEmptyCollection(), to: self.CollectionStoragePath)
// publish a reference to the Collection in storage
self.account.link<&{NFTReceiver}>(self.CollectionPublicPath, target: self.CollectionStoragePath)
// store a minter resource in account storage
self.account.save(<-create NFTMinter(), to: self.MinterStoragePath)
}
}
- 通过交易进行逻辑运行,例如这里的铸造币:
// Mint NFT
import ExampleNFT from 0x02
// This transaction allows the Minter account to mint an NFT
// and deposit it into its collection.
transaction {
// The reference to the collection that will be receiving the NFT
let receiverRef: &{ExampleNFT.NFTReceiver}
// The reference to the Minter resource stored in account storage
let minterRef: &ExampleNFT.NFTMinter
prepare(acct: AuthAccount) {
// Get the owner's collection capability and borrow a reference
self.receiverRef = acct.getCapability<&{ExampleNFT.NFTReceiver}>(ExampleNFT.CollectionPublicPath)
.borrow()
?? panic("Could not borrow receiver reference")
// Borrow a capability for the NFTMinter in storage
self.minterRef = acct.borrow<&ExampleNFT.NFTMinter>(from: ExampleNFT.MinterStoragePath)
?? panic("could not borrow minter reference")
}
execute {
// Use the minter reference to mint an NFT, which deposits
// the NFT into the collection that is sent as a parameter.
let newNFT <- self.minterRef.mintNFT()
self.receiverRef.deposit(token: <-newNFT)
log("NFT Minted and deposited to Account 2's Collection")
}
}
以上方式,大致在以太坊上生成了自己的代币。
接下来如何就是怎么把我们的币换成比特币呢?
通过托管和非托管的方式,将比特币进行代币化。当前的代币数量参考:https://btconethereum.com/
- 托管:用户将比特币发至中心化托管方,托管方存入多重签名的冷存储钱包中,并铸造WBTC代币作为返还。值得注意的是,此流程需要证明用户身份是否符合身份认证或反洗钱法规。该方法需信任铸造代币的实体,但也具有一定的安全优势。—— WBTC、HBTC
- 非托管:与包装比特币类似,但是却无需借助中心化托管方,只需通过智能合约或虚拟机即可保证资金安全并铸造代币。用户通过去信任化和无需许可的方式即可存入比特币并铸造代币化比特币 —— renBTC
思考:在交易所进行币交易是直接实现了币的转化吗?
有了能力,如何让别人愿意兑换你的币呢,依然需要为币创造价值(或者虚拟价值)
当前主流的应用形态
NFT
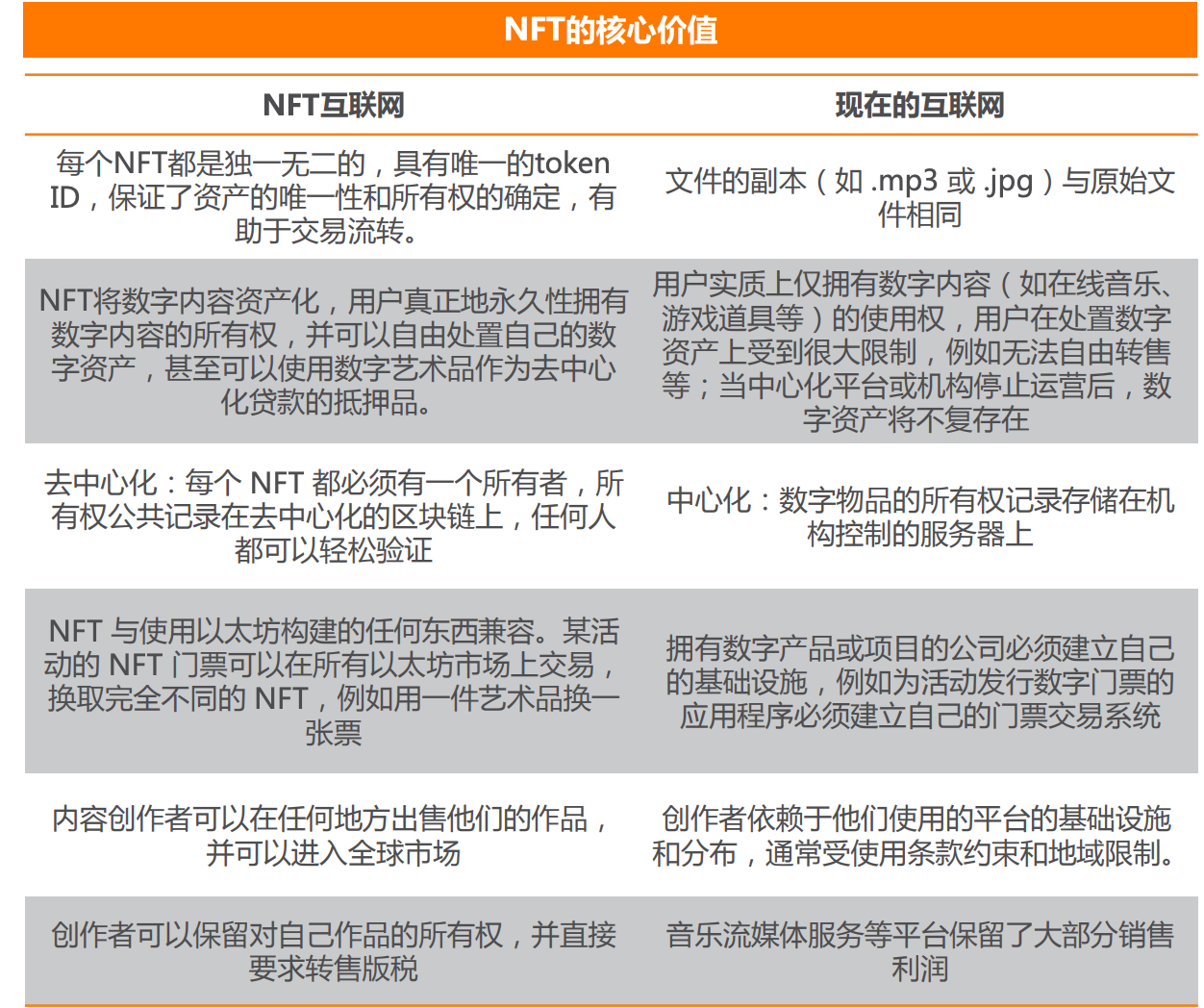
Dapp:当前热门的流行应用
最开始的NBA TOP SHOT、迷恋猫,以及最近爆火的stepn
 一双鞋,目前最便宜也得1500$
一双鞋,目前最便宜也得1500$
opensea:NFT交易
faceDAO:印度兄弟的
蚂蚁链-鲸探:蚂蚁
https://audius.co/:去中心化的音乐应用
推特创始人杰克·多西2006年第一条推文被制作成NFT后就曾被卖了290万美元,不过最近人们不太认可这条推文的价值,所以如今这条推文NFT的最新报价回落至280美元,跌了一万多倍
关于NFT的几个观点
- 现在web3.0的产品没有一个比对应的web2的产品多提供了用户价值的
- 资本力量很重要 但不是核心,算是助推剂;核心的我认为是项目方背景,他们有影响力,有人(投资方+韭菜)愿意参与。
- 真实的价值目前不明显,后续会有,当时还只是解决了上链之后的资源的ownership问题
- 从底层改变了生产关系,但是对生产力的影响现在我觉得没有,反而效率更低
即便如此,当前依然抵挡不住、从业人员、资本的青睐。中国互联网的主要矛盾从巨头与创业公司的矛盾转变成古典互联网与区块链之间的矛盾
所以当前的 web3 的核心焦点还是在去中心化,打着保护隐私、安全等一些旗号,发展一些可见不可见的能力,而在远处有一个猎人拿着枪随时准备开枪。
当前适合的区局切入点
- 娱乐化,你懂得
- 创业团队
- 个人构建链应用(像曾经的小程序,万一火了呢)